Modified by Simisola Fagbola, Econoday Economic Expert
The Economy
Monetary plan
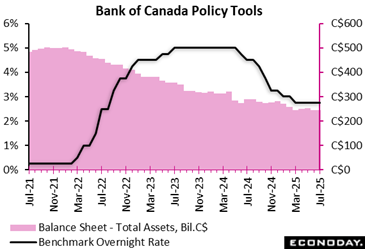
The Financial institution of Canada left its target rates of interest the same at 2 75 percent for the third successive conference, as expected by forecasters in an Econoday study. The reserve bank pointed out the resilience of the Canadian economic climate and continuous pressures on core rising cost of living, including it continues to proceed “very carefully.”
In his opening declaration of an interview adhering to the plan statement, Governor Tiff Macklem said, “At this price decision, there was clear consensus to hold our plan price the same.” The minutes of the June meeting had actually mentioned “some diversity of views on the most likely path ahead”.
The impact of profession policy and related uncertainty on Canada’s financial activity and rising cost of living continues to be the key component for the rates of interest course forward. “If a deteriorating economic situation places better descending stress on inflation and the higher rate stress from the trade disruptions are contained, there may be a requirement for a reduction in the policy rates of interest,” the BoC said.
It continues to monitor the effect of united state tolls on Canadian exports, just how this subsequently spills over to organization investment, employment and consumer spending. As it mentioned in its June declaration, the Bank additionally remains to assess the degree and speed at which services hand down boost to customers while monitoring inflation assumptions.
Generally, despite the ongoing unpredictability of U.S. trade activities regardless of some “much more concrete” components in current weeks, the reserve bank remains to avoid offering its conventional base case circumstance, providing three possible courses instead: the current situation, an acceleration situation, and a de-escalation circumstance.
Under the current circumstance based upon tolls already in place, Canada’s GDP development contracts in the 2nd quarter of 2025 It recovers to regarding 1 percent in the 2nd fifty percent of this year as exports stabilize and house costs raises progressively. Weakness proceeds next year before growth picks up to near to 2 percent in 2027 Inflation, presently at 1 9 percent, continues to be near to 2 percent throughout the perspective as higher and down stress balance out each various other.
Under the de-escalation situation, GDP development rebounds quicker and inflation is anticipated to stay below the 2 % target up until late 2026 Inflation would average around 2 percent in 2027
Under the escalation situation, growth contracts through the end of 2025 CPI rising cost of living is predicted to come to a head at simply over 2 5 % in the third quarter of 2026, before declining to around 2 percent in 2027
In all three circumstances, the neutral nominal rate is presumed to be between 2 25 percent and 3 25 percent. At 2 75 percent, the existing plan rate sits at the middle of the neutral range.
Generally, the central bank left the door available to more rate cuts to sustain growth as long as rising cost of living can continue to be under control.
The BoC made its statement as uncertainty stays around the end result of the most recent round of trade negotiations. U.S. President Donald Trump established an Aug. 1 due date for reaching a deal, without which he claimed it will certainly enforce 35 percent tariffs on Canadian goods. Head Of State Mark Carney has lately shifted his messaging to indicate that some level of tolls will stay.
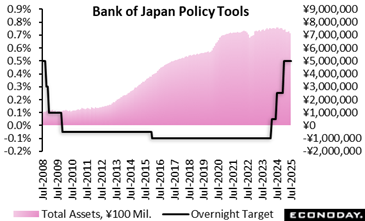
— The Bank of Japan’s nine-member board elected with one voice to preserve the target for the over night interest rate at 0. 5 % for the 4th straight meeting after treking it by 25 basis factors (0. 25 portion factor) in January amid uncertainty over profession rows.
— The bank will certainly continue raising prices if growth and rising cost of living develop in accordance with its medium-term expectation yet it is still in the procedure of stabilizing its financial plan stance from years of maintaining temporary rates near absolutely no percent.
— In its quarterly Outlook Report, the board left its development projections little bit changed for fiscal years 2025, 2026 and 2027 (ending in March 2028 while revising up its rising cost of living overview sharply for the present and seeing tame rate rises in monetary 2025 and 2026 as forecasted in the April record.
— The BOJ also noted that risks to its GDP overview is manipulated to the disadvantage, as anticipated in April, but stated dangers to its CPI projection is “typically well balanced,” contrasted to the April statement that it was skewed to the downside.
— The BOJ continues to expect Japan’s economic climate will work out about 2 % rising cost of living. “In the second half of the projection duration (fiscal 2025 with financial 2027, underlying CPI rising cost of living is most likely to be at a degree that is usually constant with the price stability target, it said, duplicating its previous report issued on May 1
The median projections by the board from its quarterly Outlook Record:
FY 25 core CPI (ex-fresh food) + 2 7 % vs. + 2 2 % in May
FY 26 core CPI (ex-fresh food) + 1 8 % vs. + 1 7 % in May
FY 27 core CPI (ex-fresh food) + 2.0% vs. + 1 9 % in May
FY 25 GDP +0. 6 % vs. +0. 5 % in May
FY 26 GDP +0. 7 % vs. +0. 7 % in May
FY 27 GDP + 1.0% vs. + 1.0% in May
— The board duplicated that “Japan’s financial development is likely to moderate” as trade and various other plans cause a downturn in abroad economic situations and to a decrease in domestic corporate revenues despite assistance from accommodative economic conditions. “After that, Japan’s economic growth rate is likely to rise, with abroad economies returning to a modest growth course,” it claimed.
— Board members advised that there are various threats to their expectation. “In particular, it remains very unclear exactly how profession and other plans in each jurisdiction will evolve and exactly how abroad financial task and rates will respond to them,” the BOJ said. “It is as a result needed to pay due attention to the impact of these developments on financial and forex markets and on Japan’s economic activity and prices.”
The FOMC left the fed funds target price variety unchanged at 4 25 to 4 50 percent, as expected. There are just small tweaks to the declaration compared to that provided at the prior conference. The declaration noted the continuing impact that the unusual movements in worldwide profession have actually had on the GDP information and provided a somewhat less positive evaluation of economic task. There was no change in the language concerning the labor market and rising cost of living. The declaration stated, “Although swings in web exports continue to influence the information, recent indicators suggest that growth of economic task moderated in the first fifty percent of the year. The unemployment rate stays reduced, and labor market conditions stay solid. Rising cost of living stays somewhat raised.”
The statement also stated, “Unpredictability concerning the economic overview remains elevated.” The language around decreased uncertainty in the prior declaration was removed.
The ballot at the end of the meeting consisted of two dissents from Governors Michelle Bowmand and Christopher Waller that both favored a 25 basis factor cut in the fed funds price. It is unusual for a governor to dissent, and two guvs have actually not dissented in a meeting vote given that the 1990’s. The ballot was 9 – 2 with Guv Adriana Kugler missing and not voting.
Employment
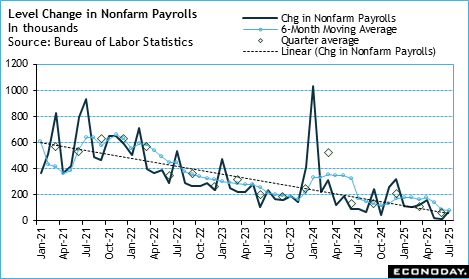
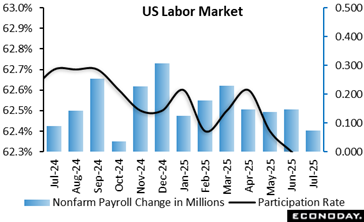
The regular monthly United States employment record has considerable alterations that paint problems in the labor market as much weak than formerly thought and reshapes the expectation for monetary policy. The rapid air conditioning in employing and small increase in the joblessness rate make a rate cut at the September 16 – 17 FOMC conference much more most likely unless the following round of inflation records are especially startling.
Nonfarm pay-rolls are up 73, 000 in July after increases of 14, 000 in June and 19, 000 in May. July nonfarm pay-rolls are listed below the agreement of up 110, 000 in the Econoday study of forecasters. The July boost is not materially various from the second quarter monthly standard of up 64, 000, or the six-month moving average of up 81, 000 Nonetheless, the last 3 months of hiring represents a sudden slowdown from the 4th quarter 2024 standard of up 209, 000 and first quarter 2025 standard of up 111, 000
The BLS kept in mind, “Revisions for May and June were bigger than typical. The modification in overall nonfarm payroll employment for May was modified down by 125, 000, from + 144, 000 to + 19, 000, and the modification for June was revised down by 133, 000, from + 147, 000 to + 14, 000 With these alterations, employment in May and June combined is 258, 000 less than formerly reported.”
Private pay-rolls are up 83, 000 in July. Goods-producers’ payrolls are down 13, 000 with manufacturing down 11, 000 and extracting down 4, 000, while construction added 2, 000 jobs. Service-providers added 96, 000 tasks in July, the majority of which are from employing 73, 300 in healthcare and social assistance.
Federal government tasks are down 10, 000 in July as a result of declines of 12, 000 at the government level and 3, 000 in city government. State controling hiring is up 5, 000
Average per hour revenues are up 0. 3 percent in July from June and up 3 9 percent year-over-year. Regular monthly rises in ordinary hourly earnings stay small and the year-over-year modification has actually been essentially the same since January.
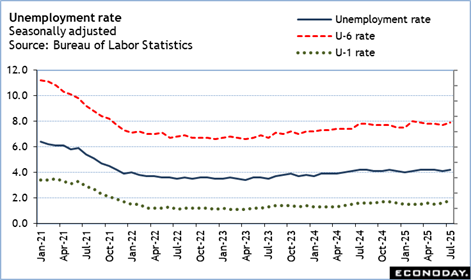
The unemployment price is up a tenth to 4 2 percent in July because of a 260, 000 decrease in the variety of people employed and a boost of 221, 000 in the number of jobless. The U- 6 rate– the broadest step of joblessness– is up two-tenths go 7 9 percent in July and shows much more employees are dissuaded regarding locating tasks.
GDP
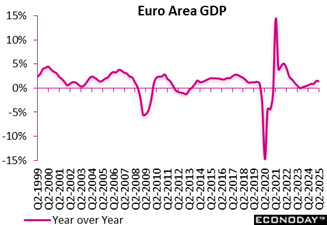
Financial development in the euro area cooled somewhat in the 2nd quarter of 2025, with GDP bordering up by simply 0. 1 percent contrasted to the previous quarter, a concealed contrast to the projections of minus 0. 1 percent. This notes a notable downturn from the initial quarter’s stronger 0. 6 percent expansion, hinting at expanding caution throughout the bloc amid relentless economic unpredictability.
Year-over-year, the economic climate preserved moderate momentum, with GDP increasing by 1 4 percent, a mild dip from the previous quarter’s 1 5 percent. This recommends that, while the region stays on a growth path, it is navigating an extra delicate recovery phase, showing financial plan and profession uncertainties impacting the bloc.
Within the area’s quarterly advancement, France broadened 0. 3 percent after 0. 1 percent, while Spain grew 0. 7 percent after 0. 6 percent. Nonetheless, Germany fell by minus 0. 1 percent after 0. 3 percent, while Italy also fell by minus 0. 1 percent after 0. 3 percent.
These updates use an early signal that the eurozone’s recovery is still intact, though losing pace. The minimal quarterly gain highlights the demand for vigilance among policymakers and investors, particularly as customer confidence and financial investment view end up being extra important in steering the region’s temporary economic direction.
United state financial task recoiled in the 2nd quarter of 2025, as the considerable drop-off in goods imports, coupled with a significant increase in consumer investing, drove the rise in genuine GDP. Additional factor for the Federal Reserve to resist on reducing the government funds rate at the verdict of the FOMC meeting today.
Q 2 GDP enhanced by 3 percent, greater than balancing out the 0. 5 percent decrease in the first quarter and defeating assumptions for a 2 5 percent increase in the Econoday study of forecasters.
Customer costs as determined by Personal Usage Expenses was up 1 4 percent in Q 2 adhering to simply a 0. 5 percent uptick in the first quarter, while the need for imports dove 30 3 percent after Q 1’s 37 9 percent rise.
Nevertheless, exports were additionally down last quarter– tempering the boost in economic activity. The decrease was by 1 8 percent, negating 0. 4 percent growth in the first quarter. Gross domestic personal financial investment additionally plunged, down 15 6 percent– over half of Q 1’s 23 8 percent dive.
United States Review
Weak Jobs Report Puts Price Cut Down on Table for September
By Theresa Sheehan, Econoday Financial Expert
The July Work Situation offers a big drawback shock. Not only was the 73, 000 boost in nonfarm pay-rolls listed below the Econoday consensus forecast of up 110, 000, yet there was a substantial internet revision lower of 258, 000 for the prior two months. The average increase in July payrolls in addition to the reset to work gains in the past 2 months changes the expectation for monetary plan.
The FOMC will need to reassess the dangers to maximum work, specifically if the initial criteria modification set up for launch on September 9 likewise affirms that task gains are lower than formerly assumed. Had the July employment data been available on July 30, a rate cut would certainly have been nearly ensured. As it is, the Fed policymakers might discover the dangers to inflation from tolls are less compelling when they next satisfy on September 17 – 18 Of course, this will certainly be dependent on the information records set for launch in the intermeeting duration.
In any case, hiring has actually cooled down quickly and dramatically, and to the factor where it suggests that businesses are not just not working with but that they will certainly soon be reducing current staffing.
The one-tenth uptick to 4 2 percent in the July unemployment rate is well within typical month-to-month variant. Nevertheless, it should not be dismissed out of hand. In the context of the two-tenths climb in the U- 6 unemployment rate to 7 9 percent, it seems like the start of an upward fad. The unemployment price has actually secured at 4 2 percent in four of the previous 5 months and goes to the top of the narrow range of 4.0 percent to 4 2 percent that has actually dominated for the previous 20 months.
It is also notable that the joblessness rate for those jobless 15 weeks or longer depends on 1 8 percent in July after 1 6 percent in June and 1 5 percent in May. Durations of unemployment are extending.